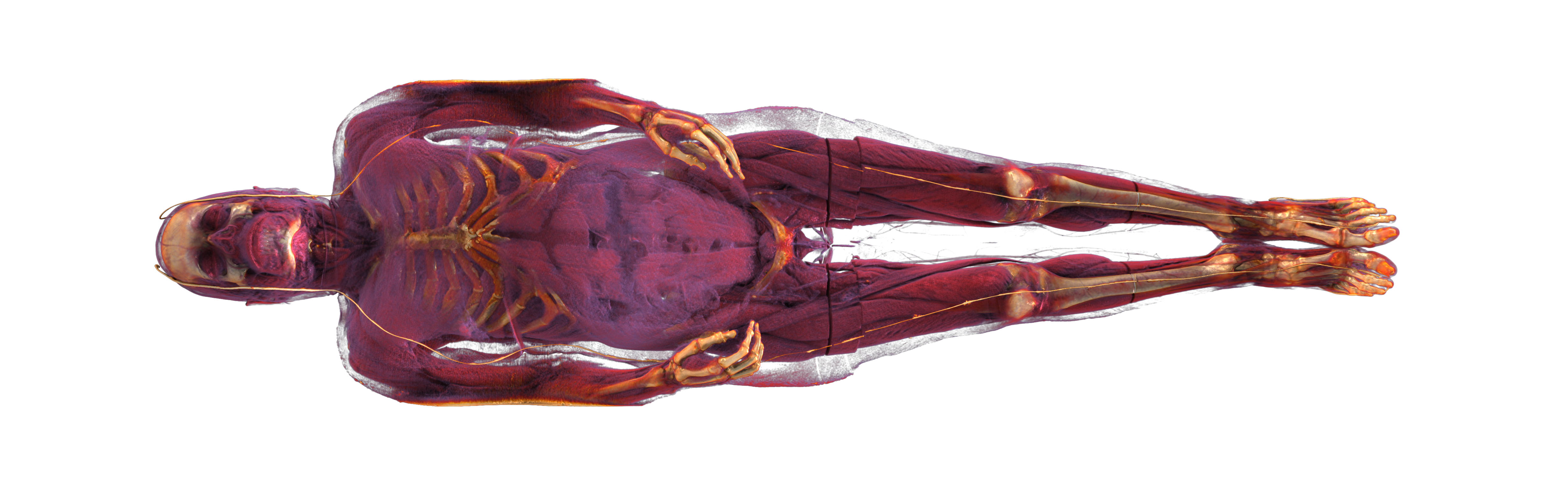
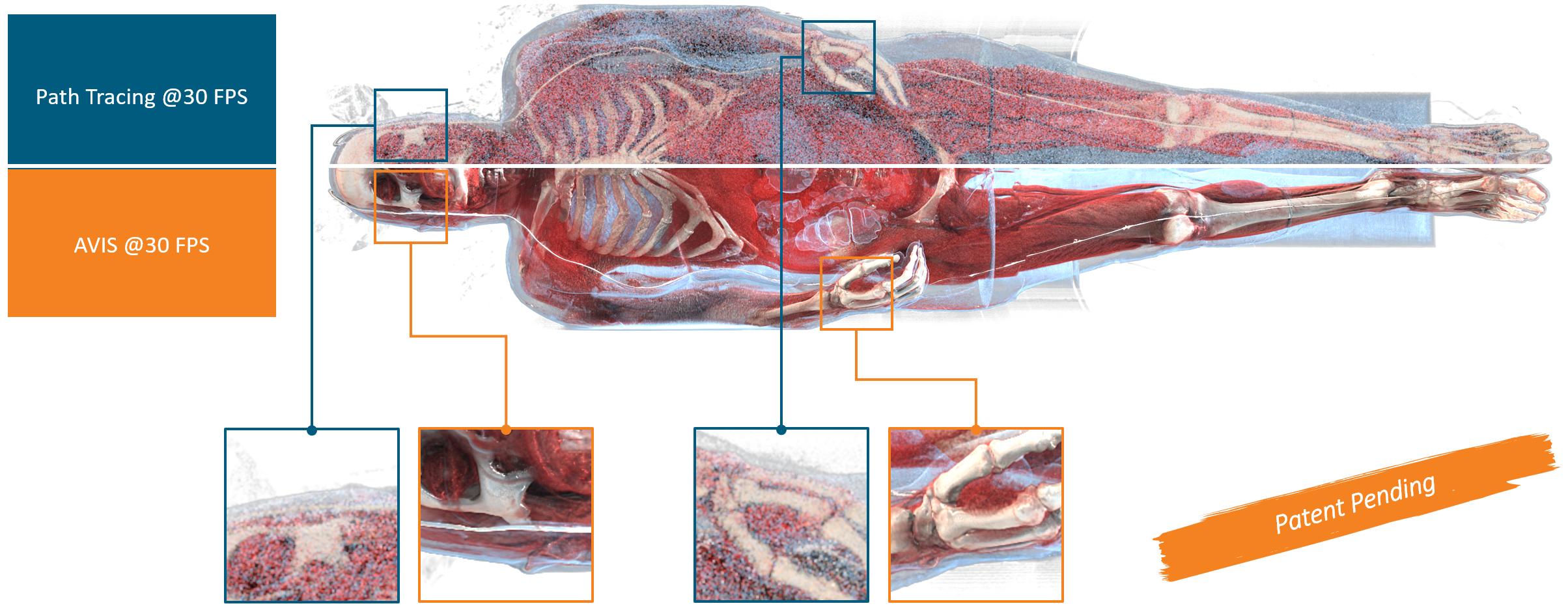
Direct volume rendering is a key technique for the visualization of medical image data. It allows to display the image data as acquired by a CT or MRI in a three dimensional rendering without the need for segmentation and mesh creation. Since it displays all the available data in the volumetric data depending on a transfer function, it offers more context than mesh based visualization. Advanced techniques, such as Path Tracing, allow to simulate realistic lighting and shadowing, but often suffer from low frame rates, image noise or other restrictions with regard to interactive changes of the camera, clipping planes, or the transfer function.
Volume Rendering
Related Publications
„Adaptive Illumination Sampling for Direct Volume Rendering“. Advances in Computer Graphics. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp 107–118 (2020)
(Authors: Kraft V, Link F, Schenk A, Schumann C)
"A Clinical User Study Investigating the Benefits of Adaptive Volumetric Illumination Sampling“. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (2024)
(Authors: Kraft V, Schumann C, Salzmann D, Weyhe D, Zachmann G, Schenk A)
 Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Medicine MEVIS
Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Medicine MEVIS